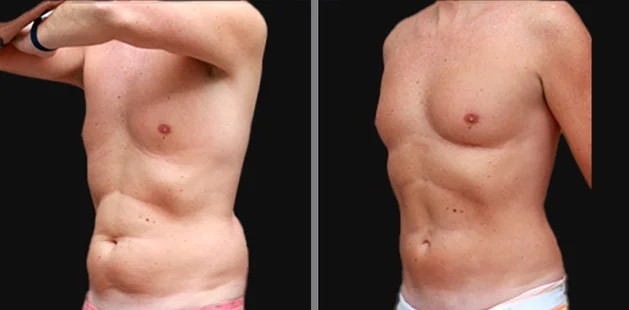
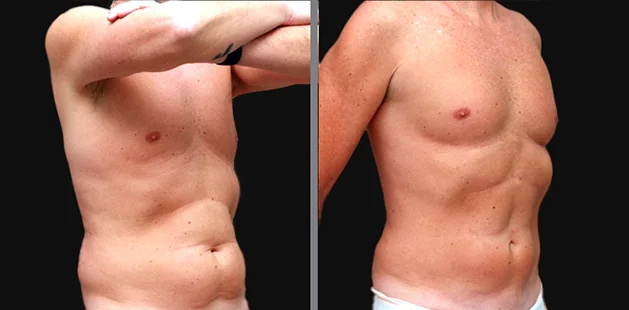
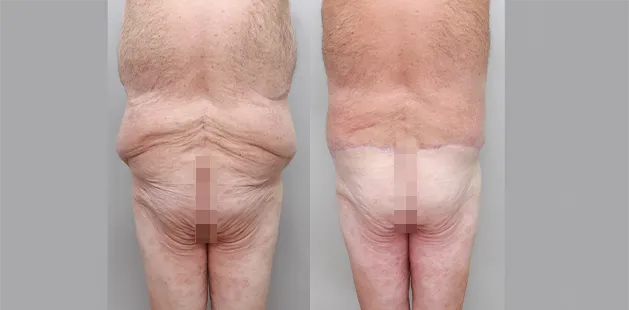
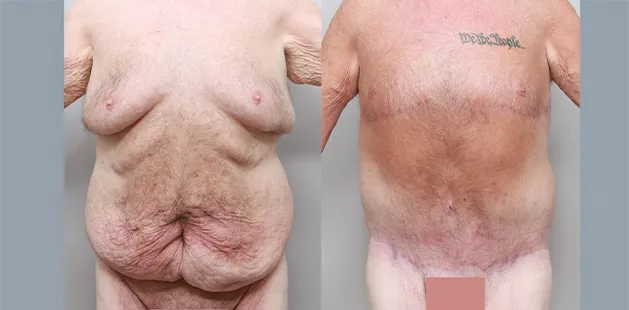
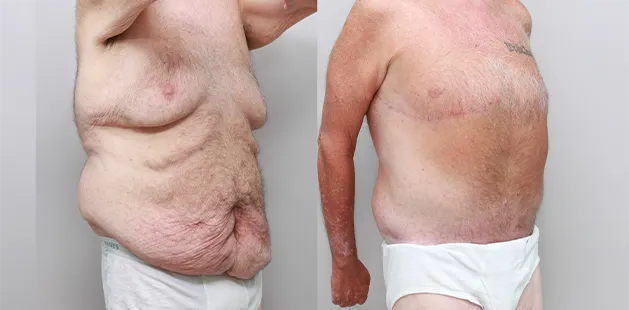
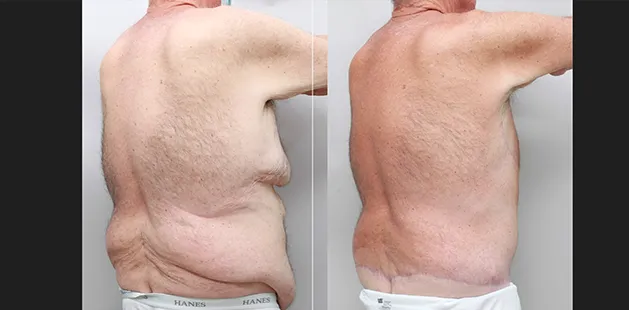
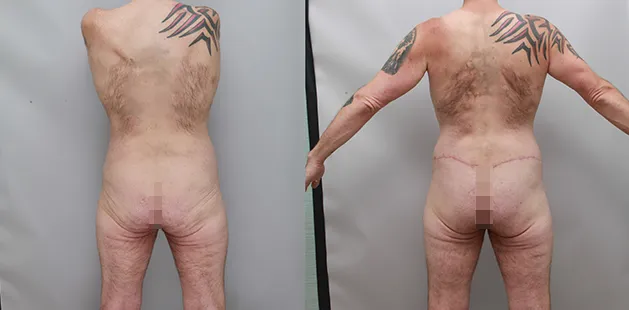
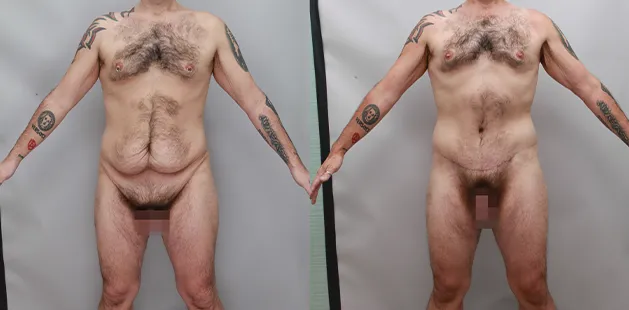
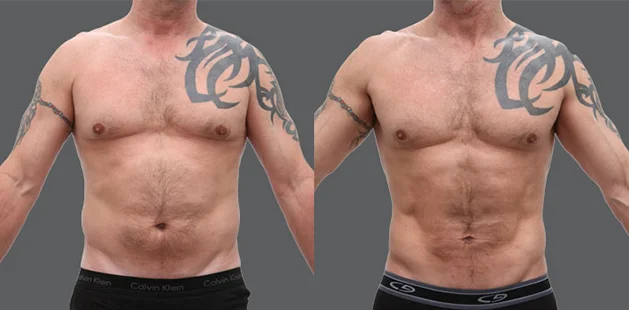
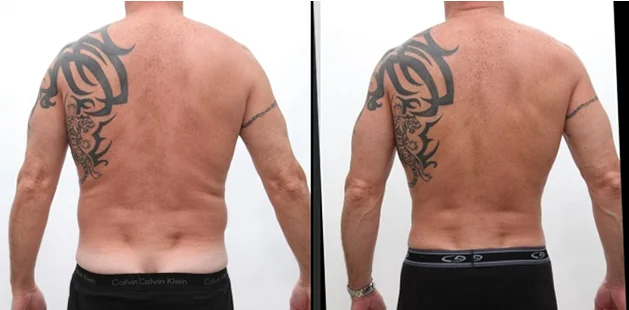
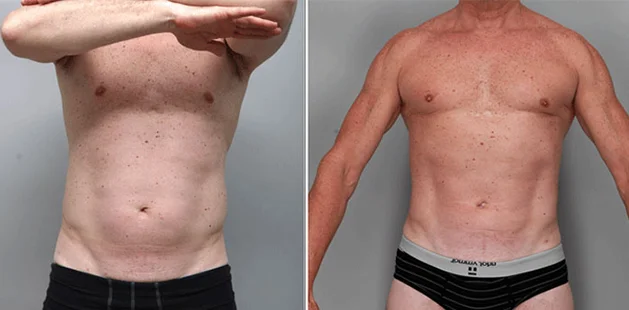
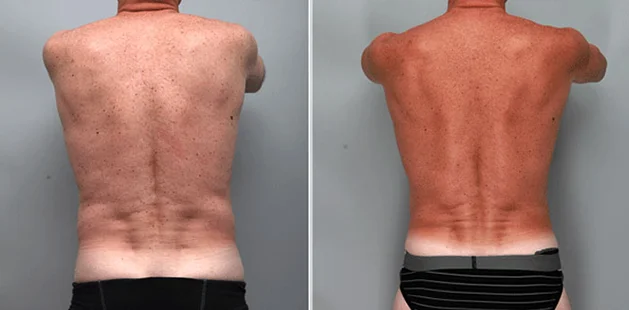
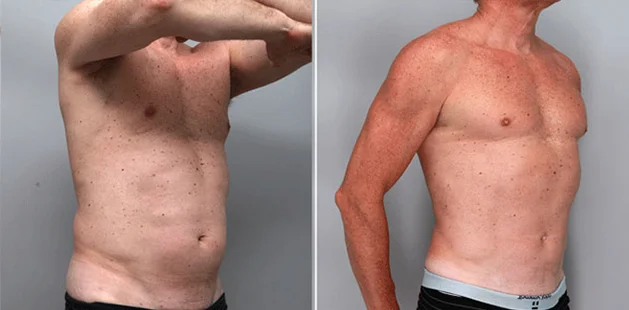
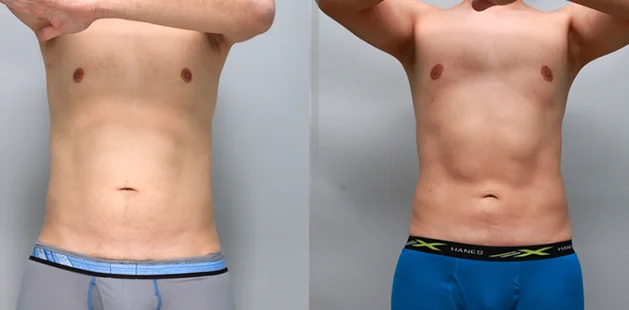
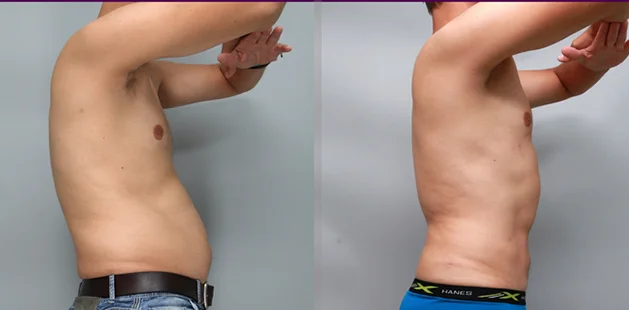
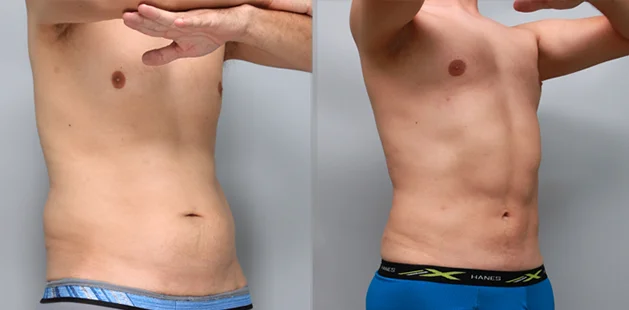
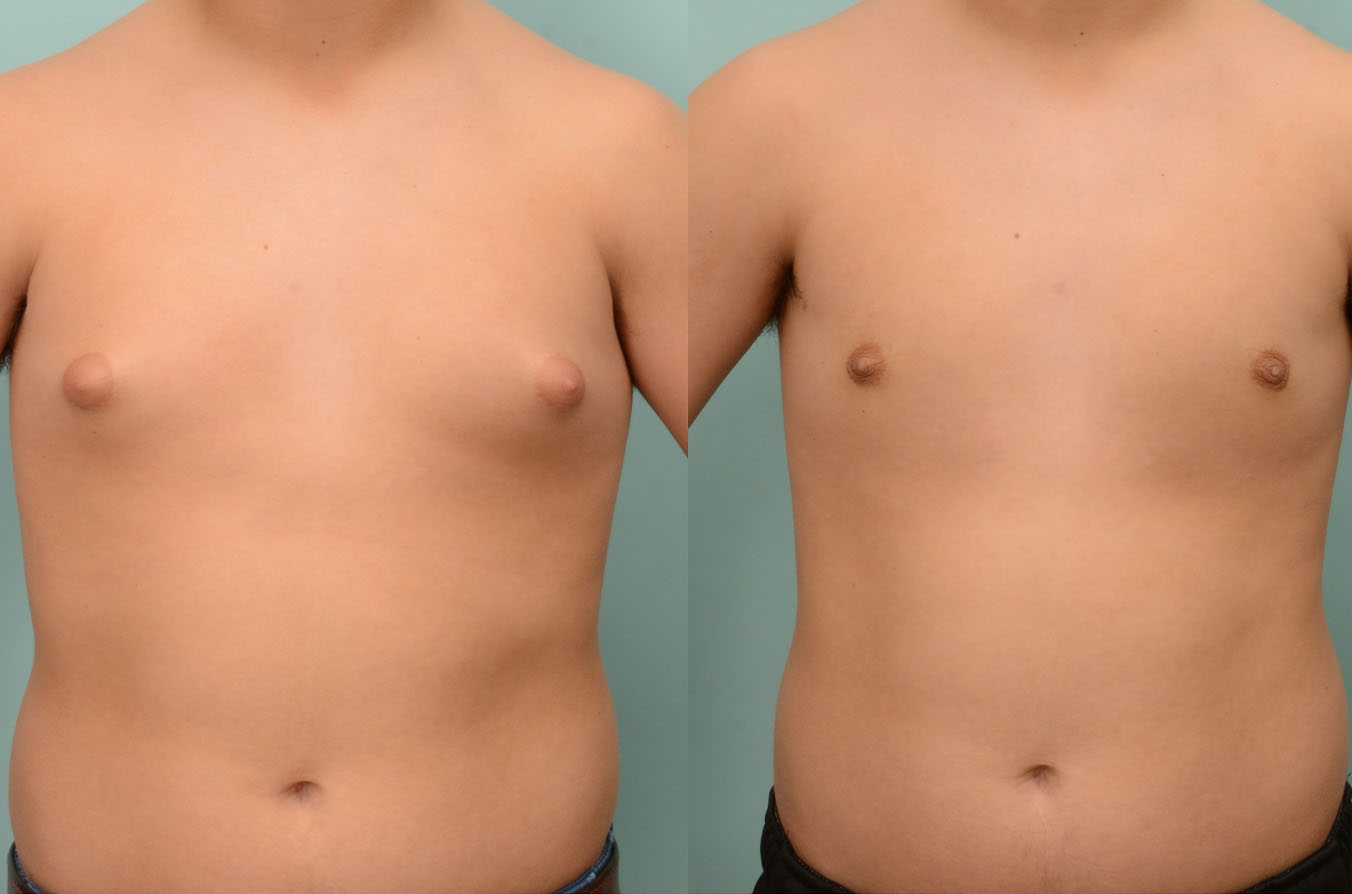
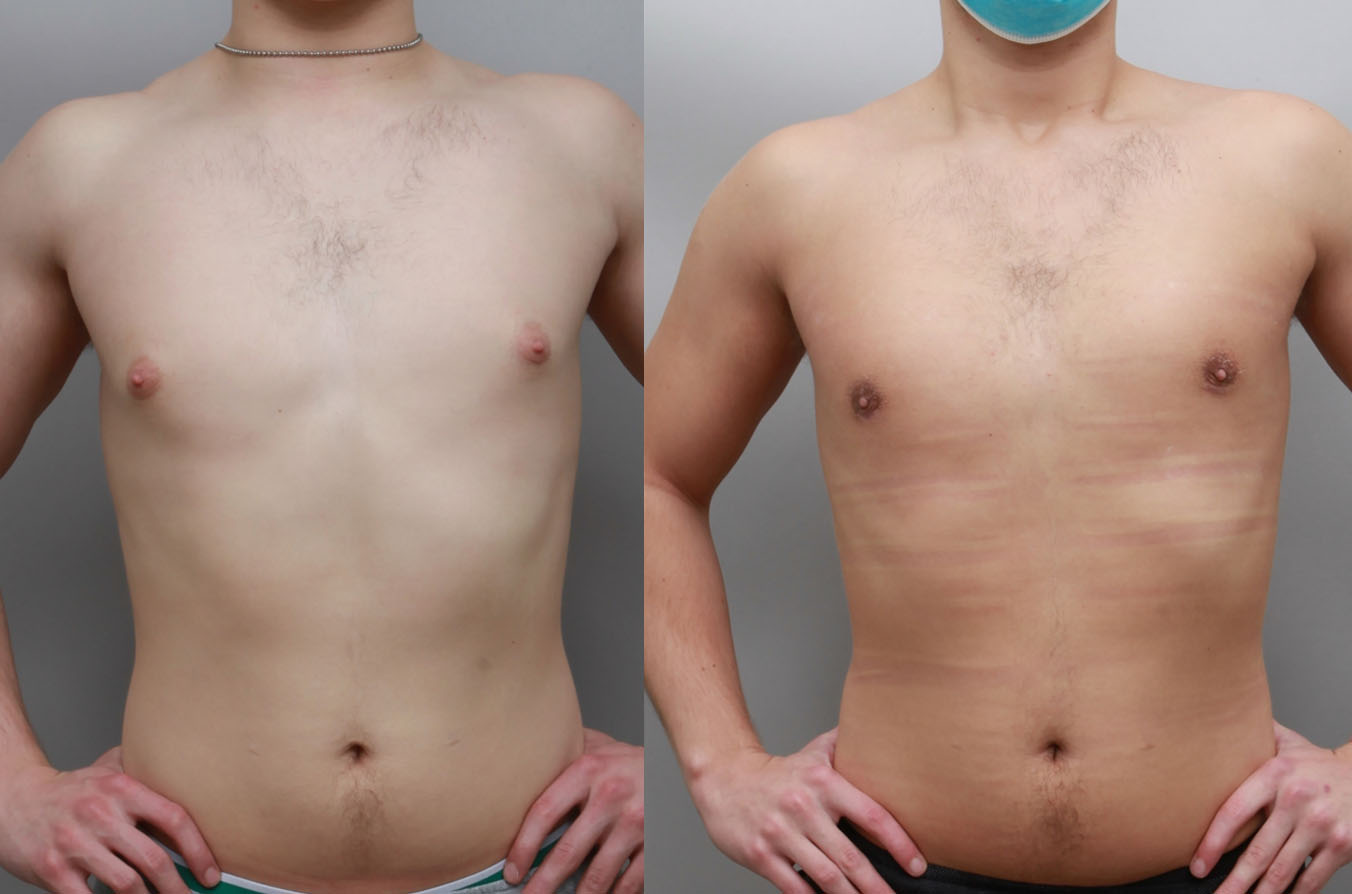
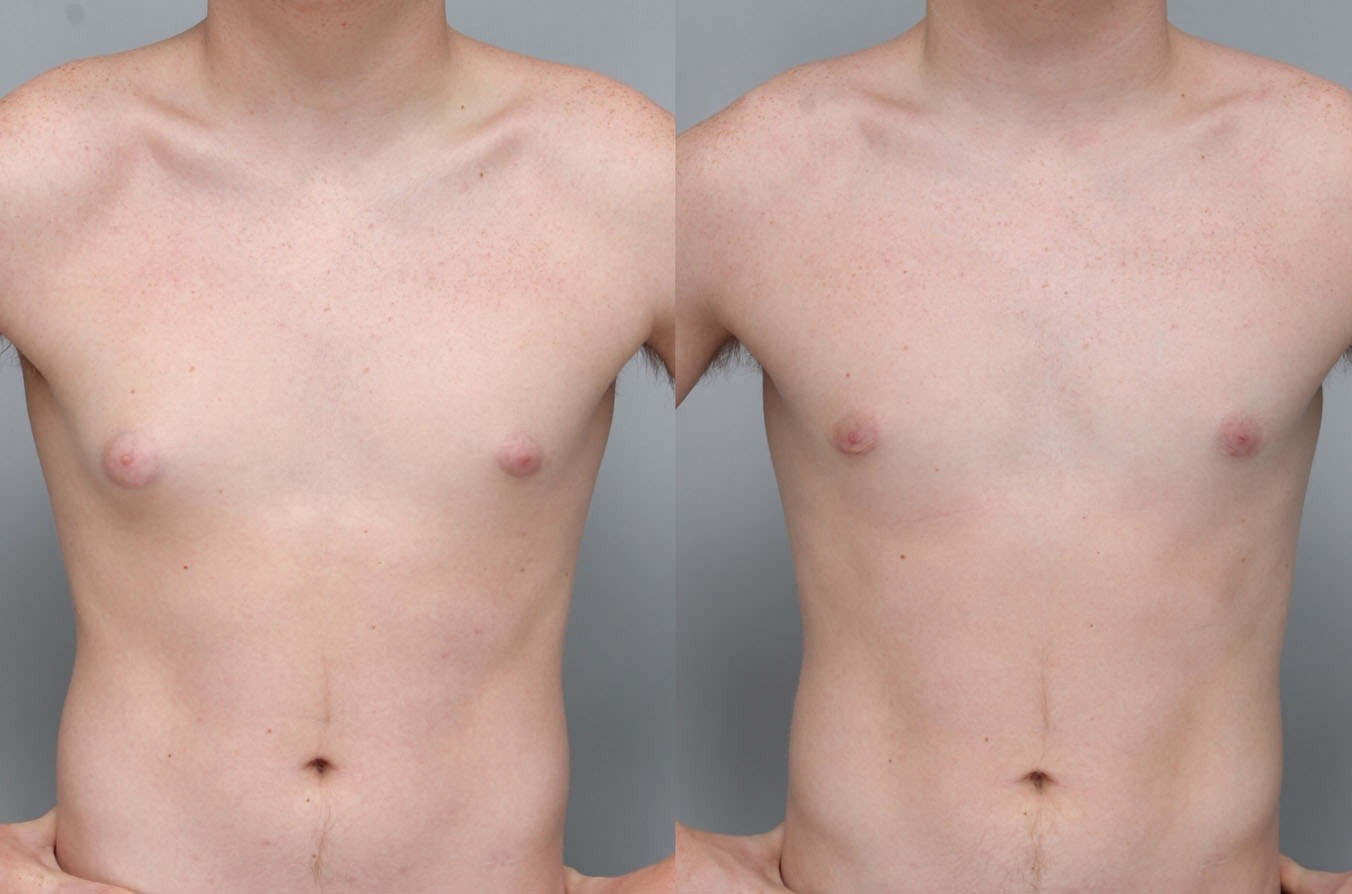
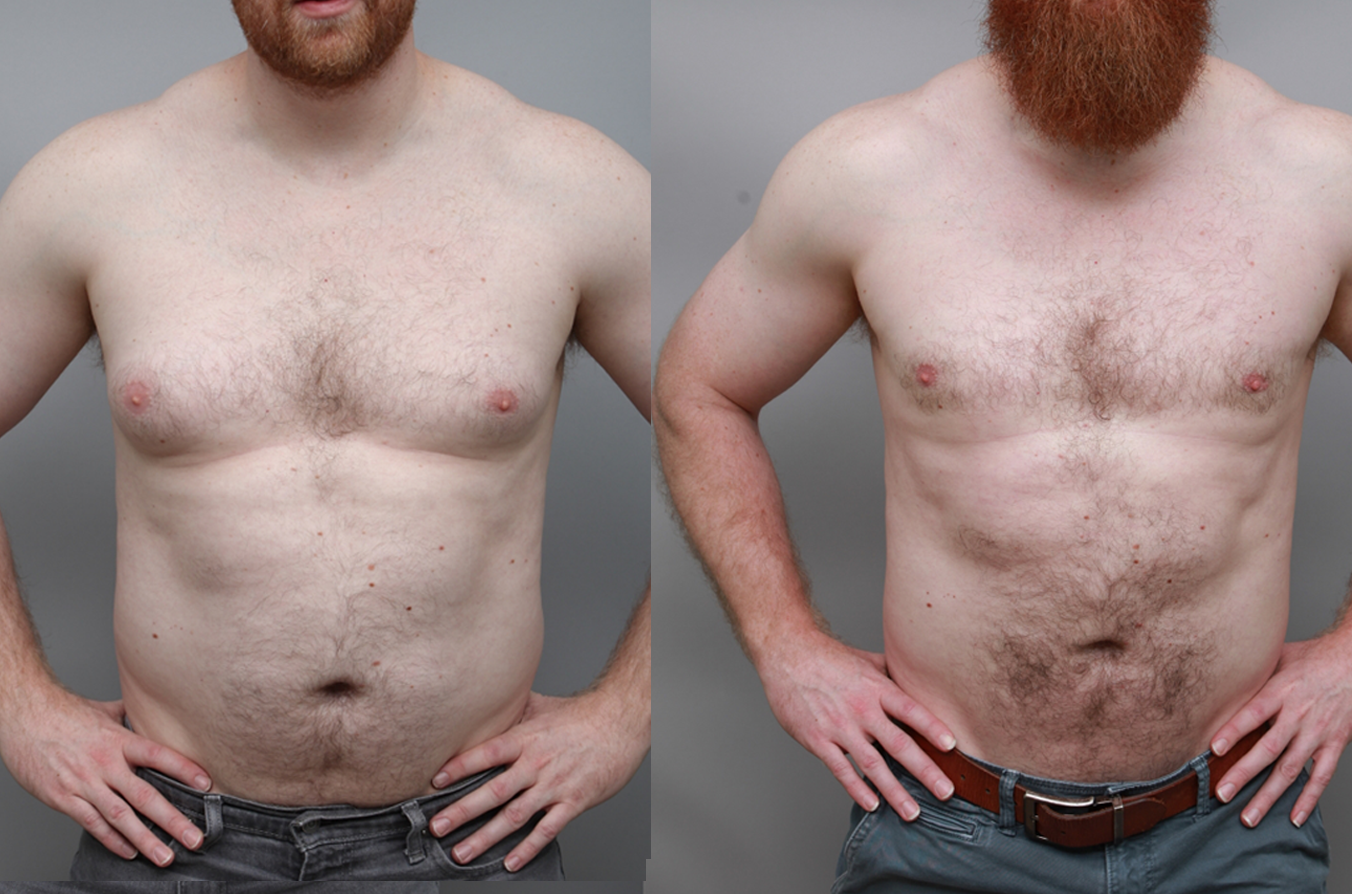
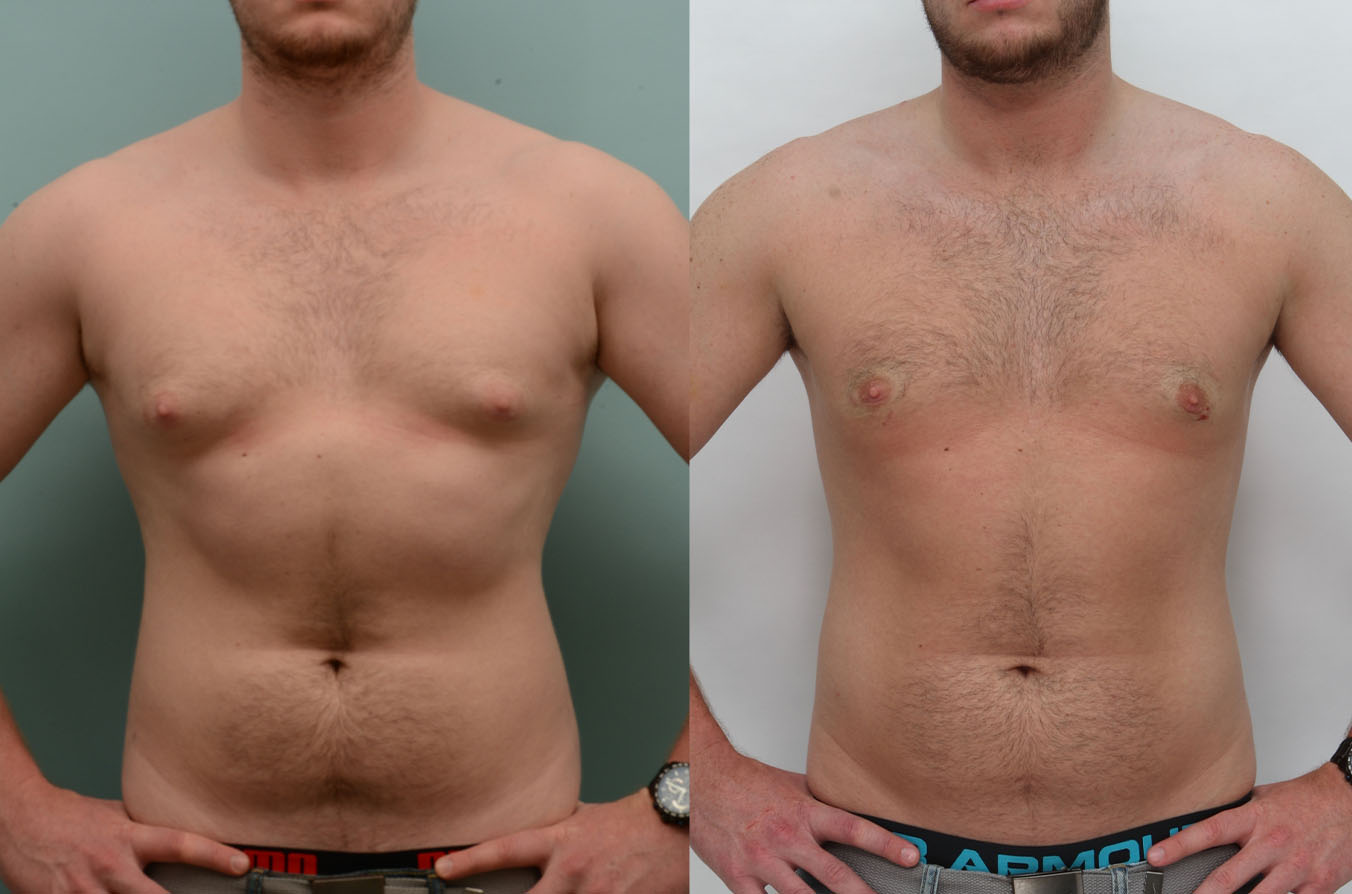
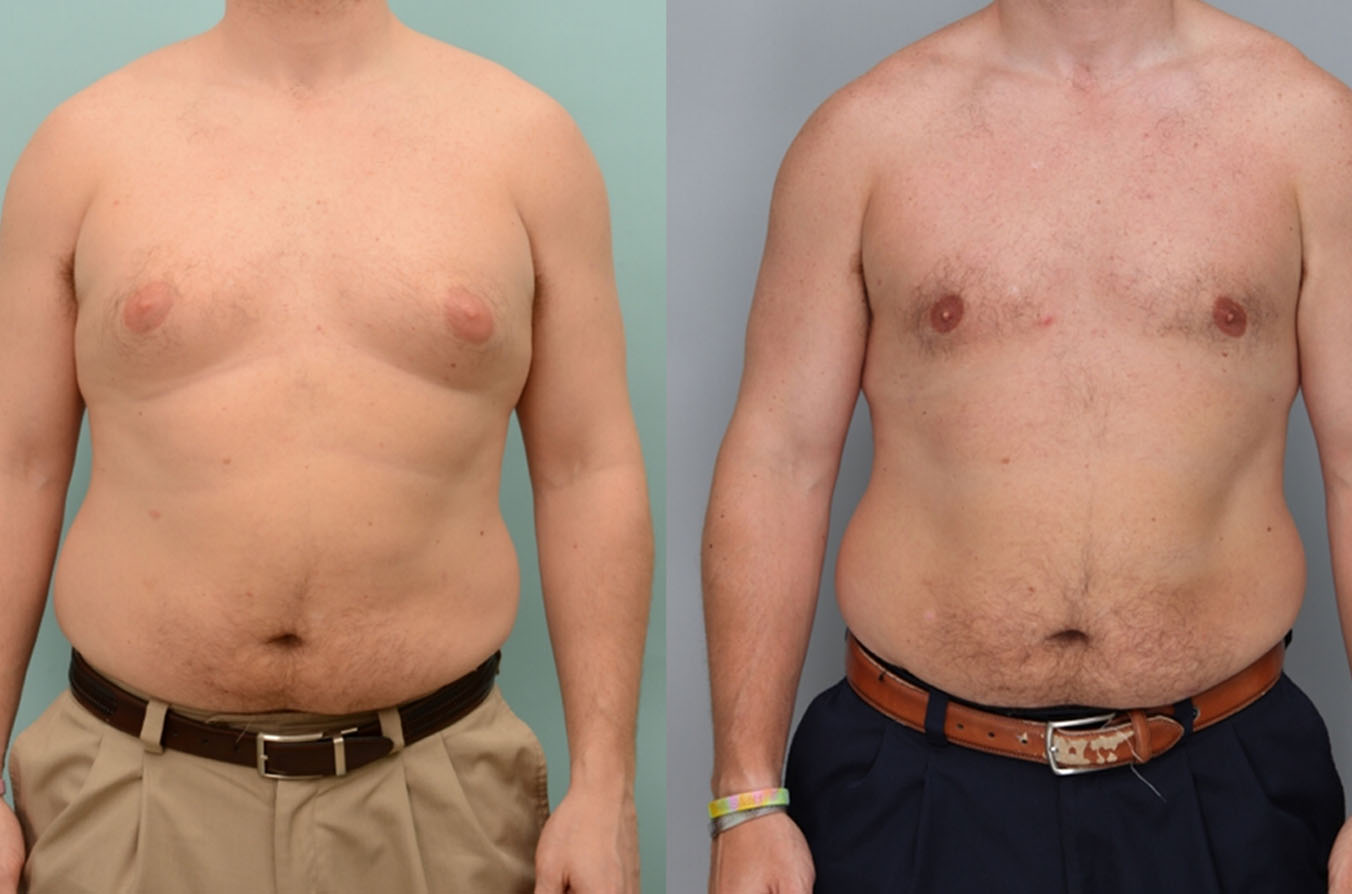
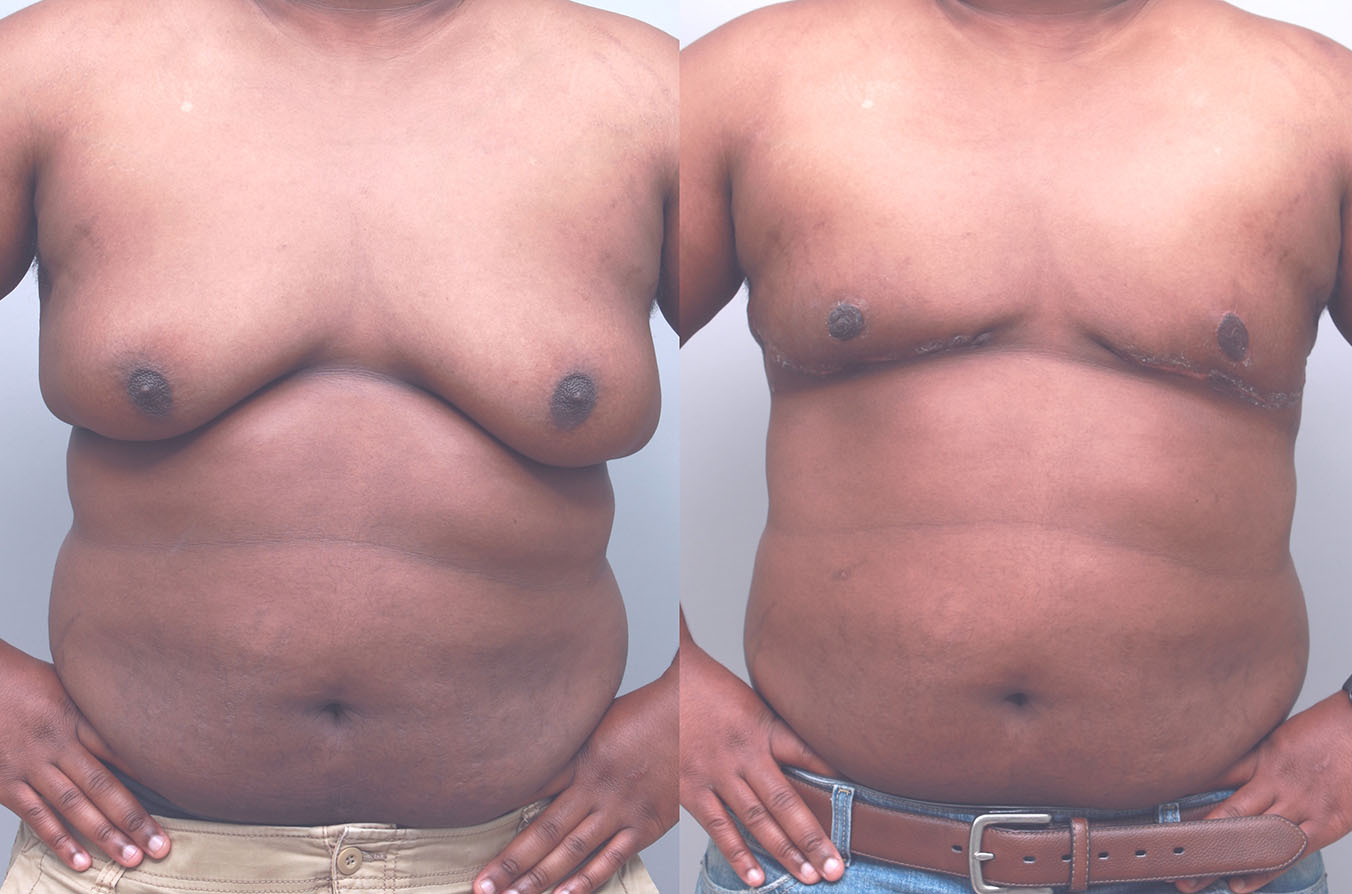
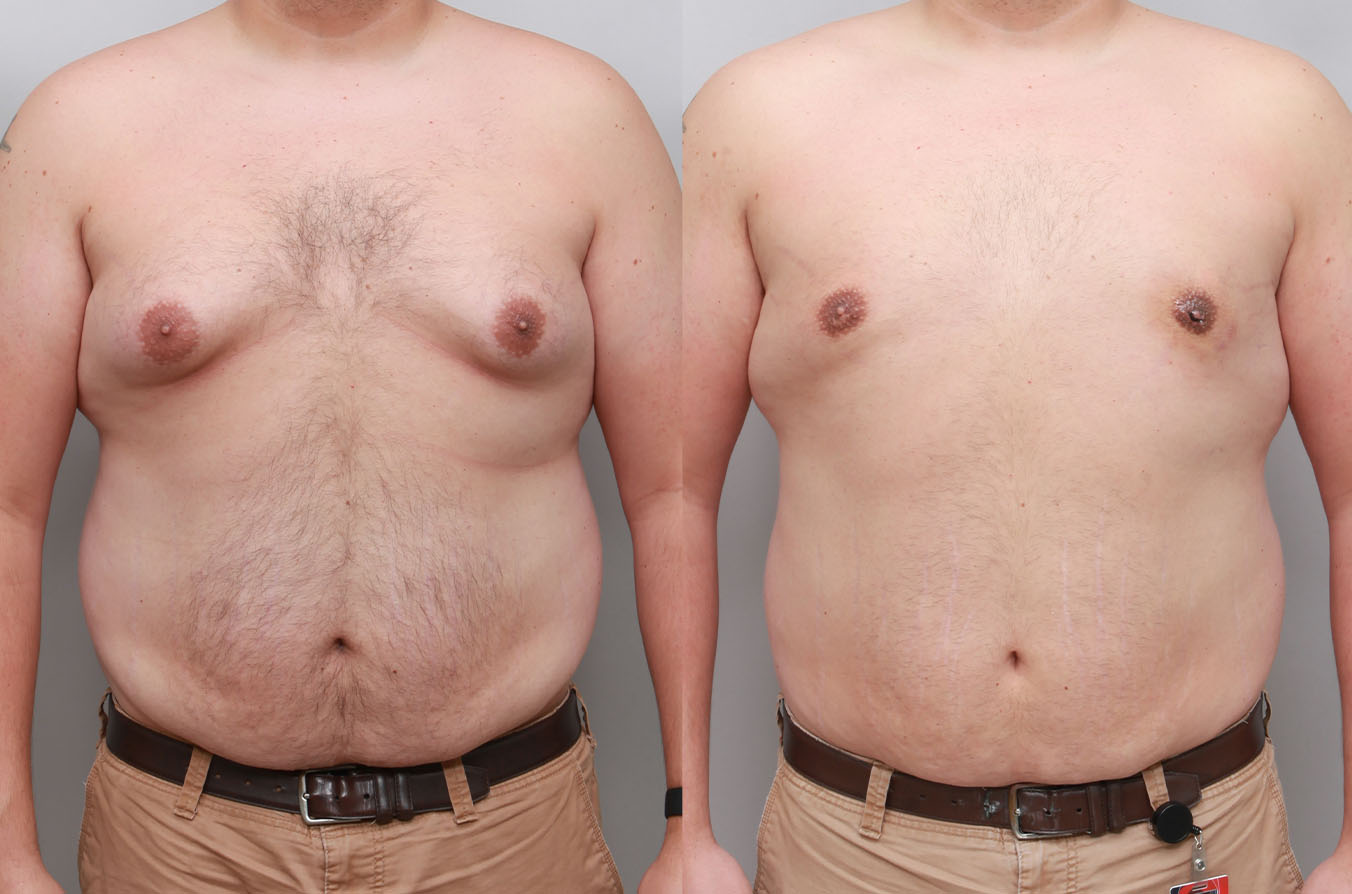
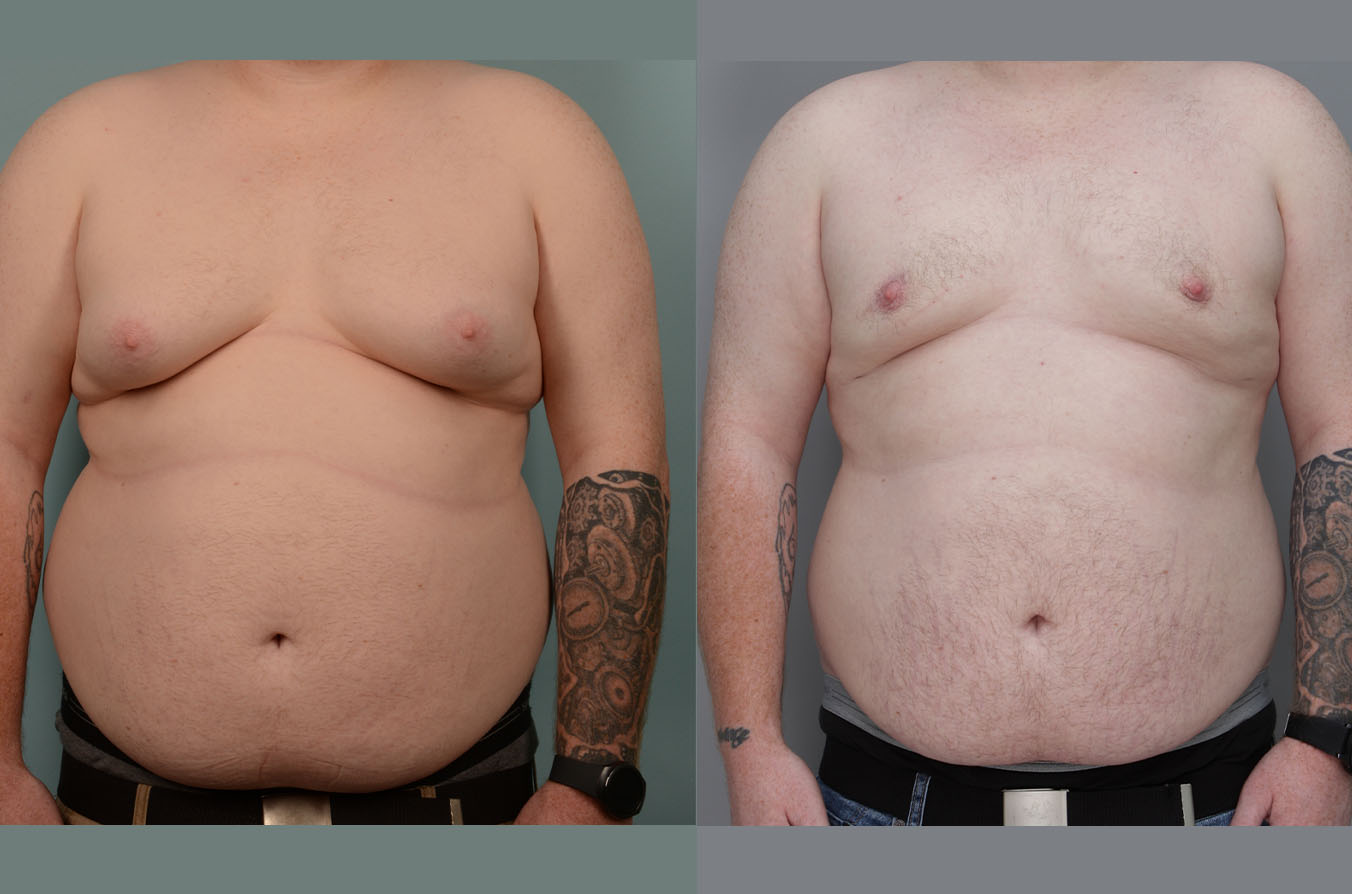
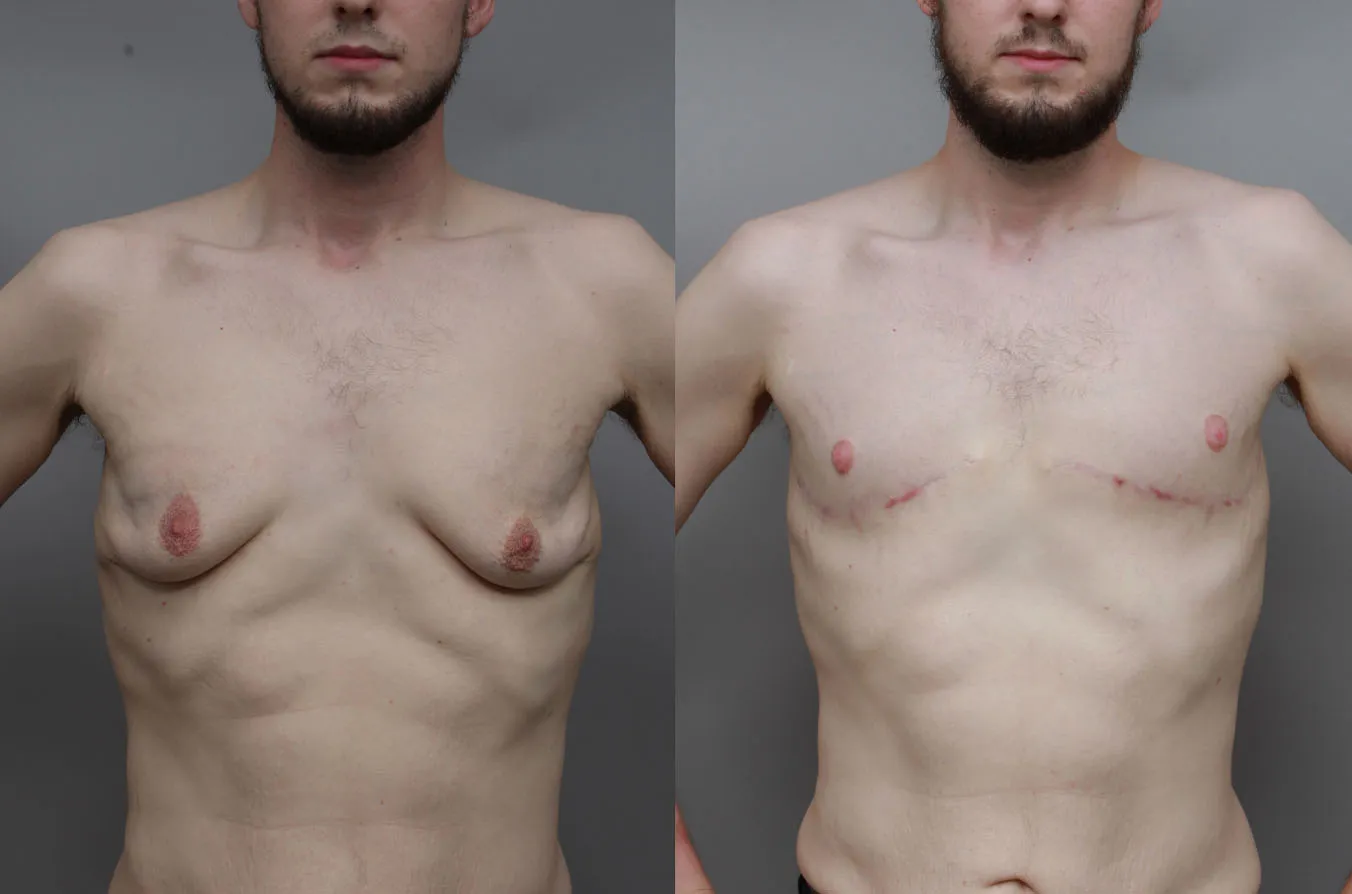
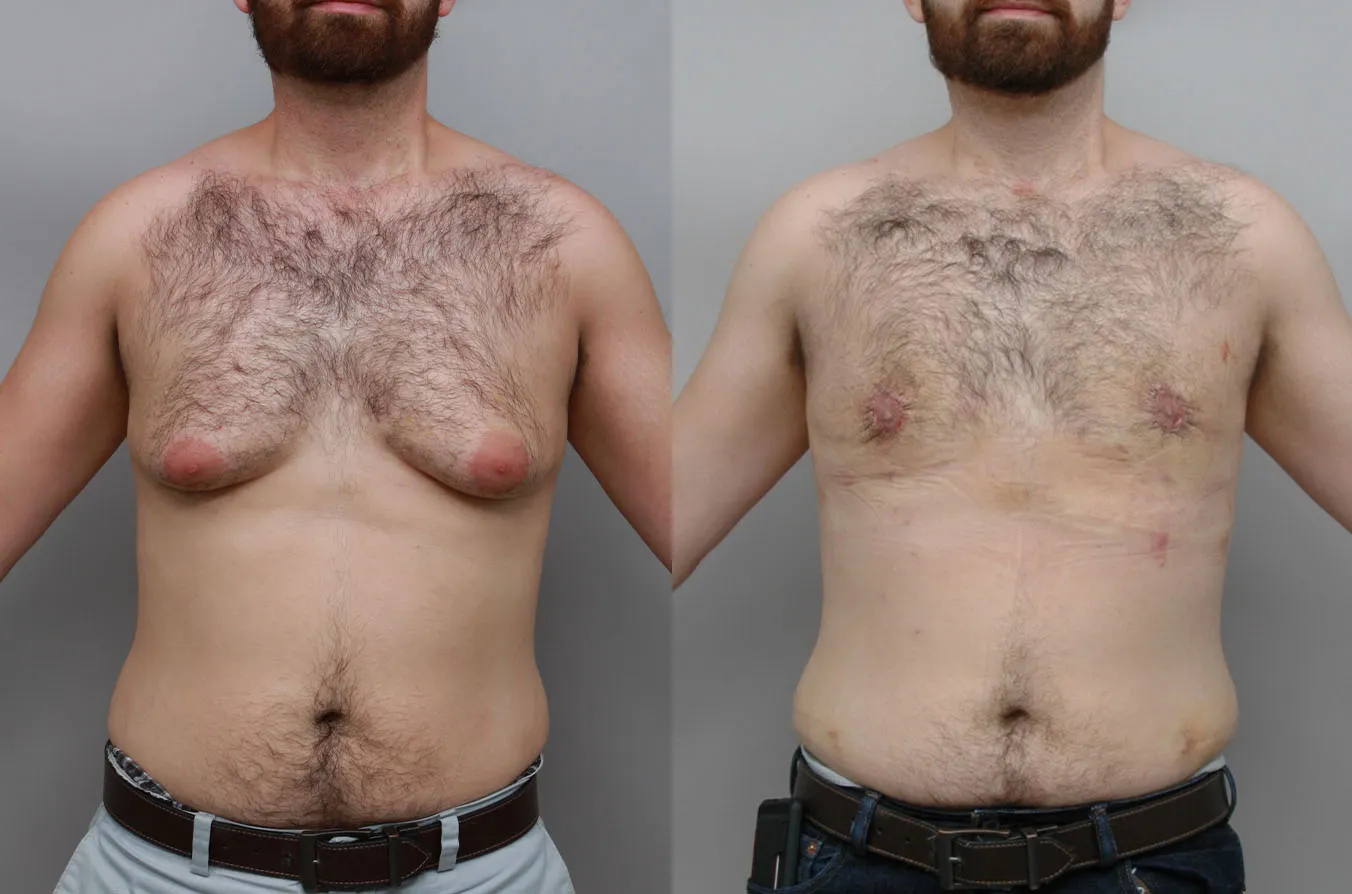
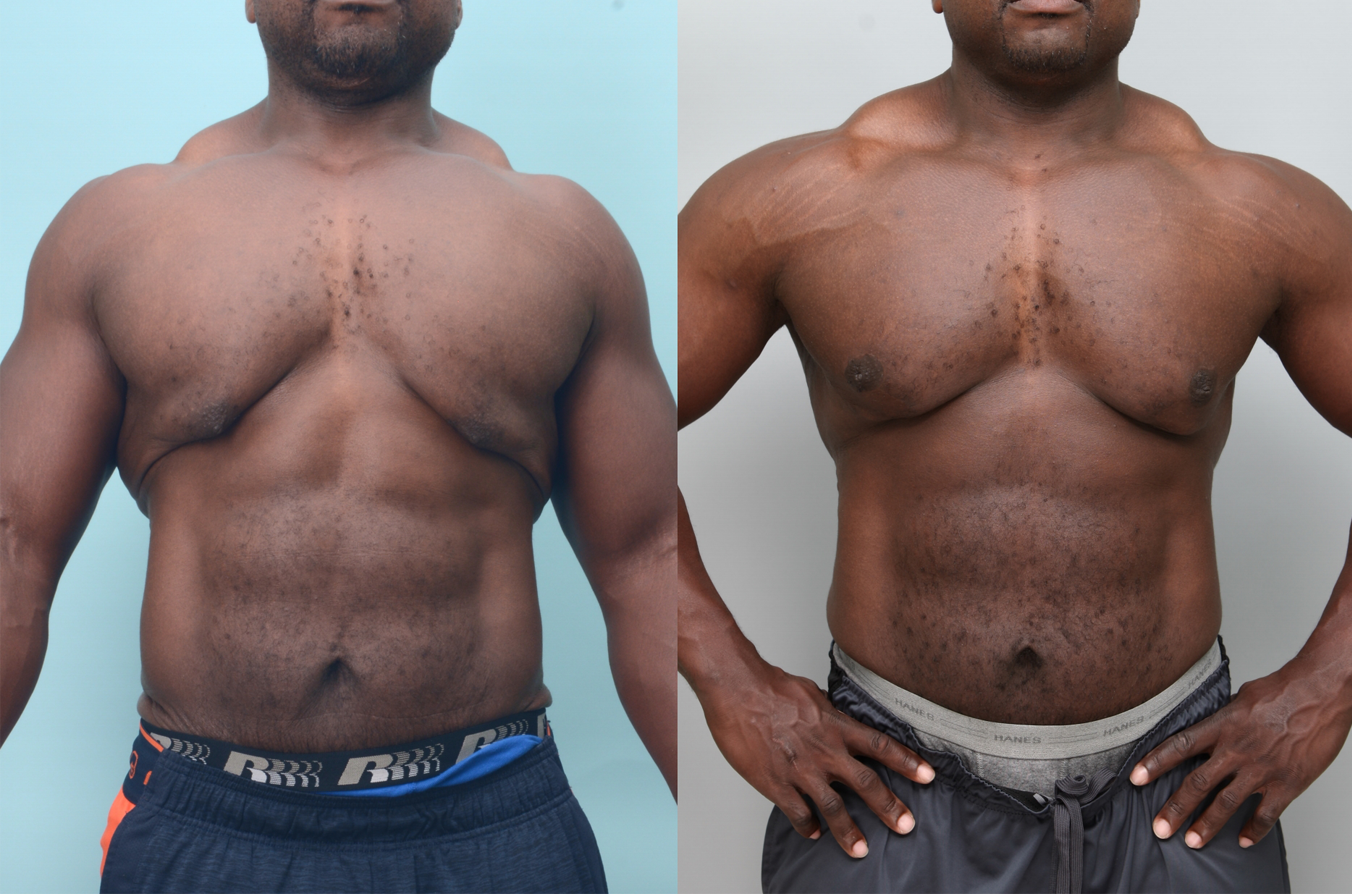
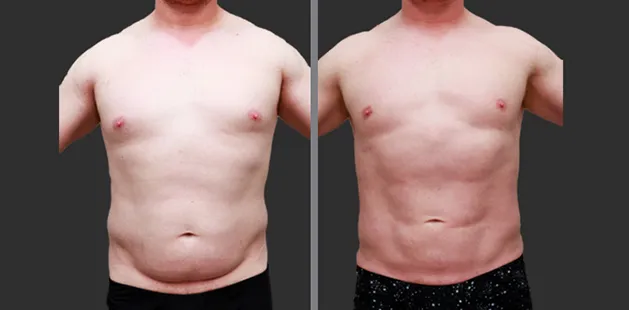
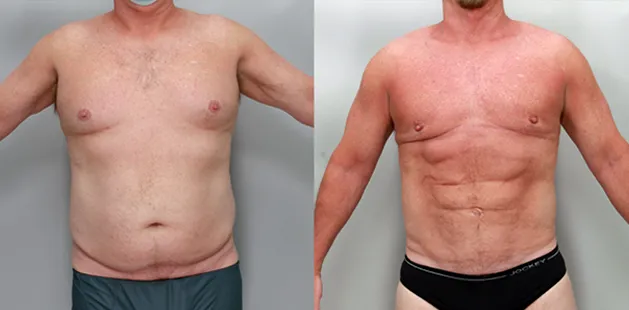
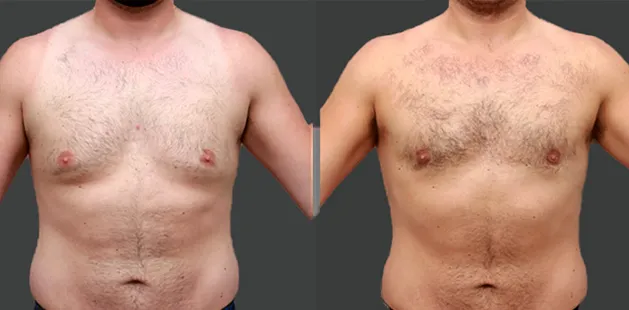
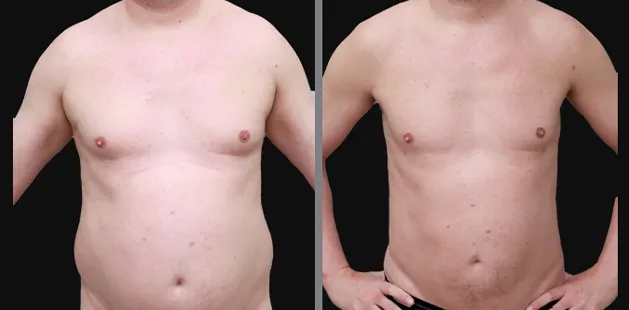
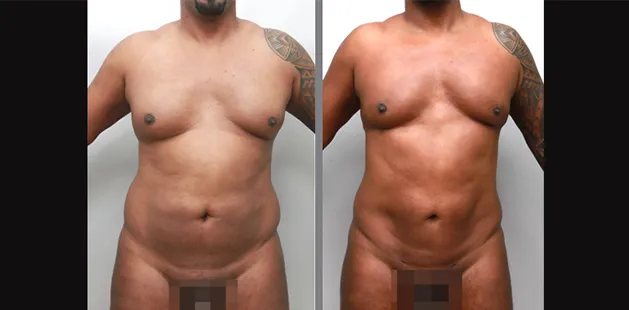
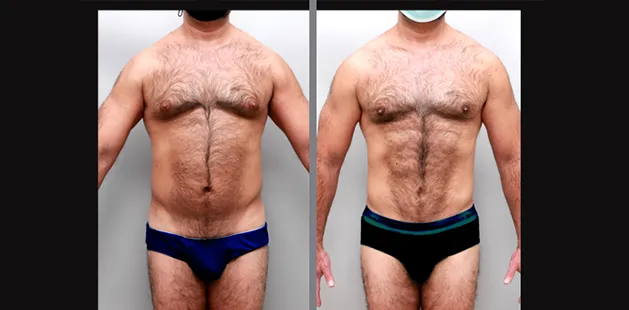
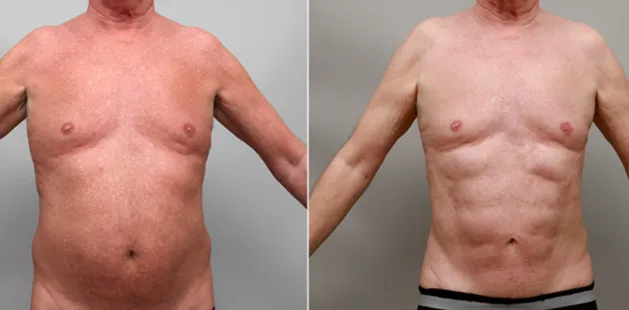
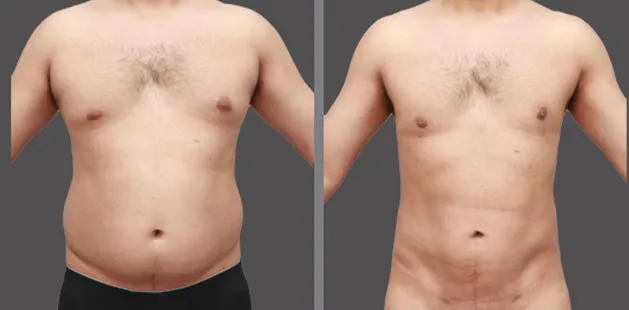
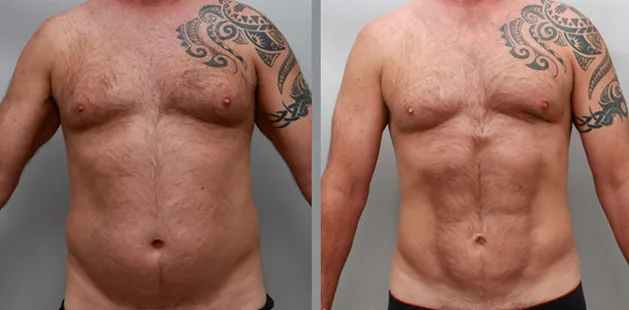
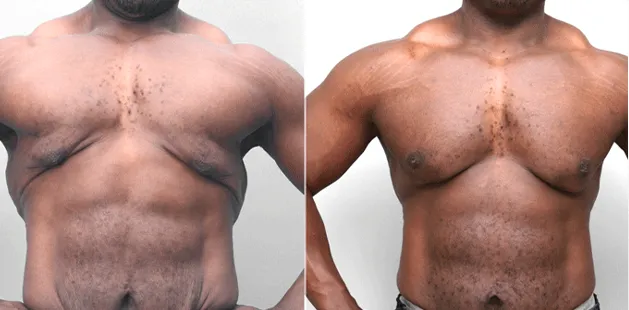
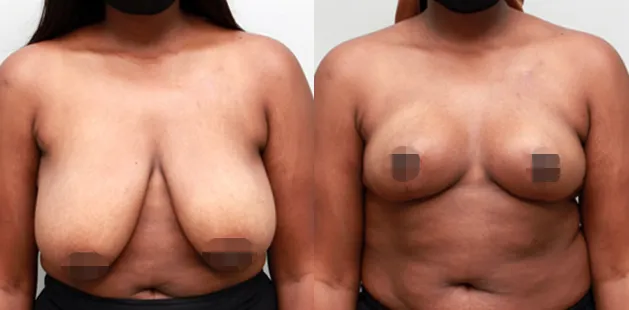
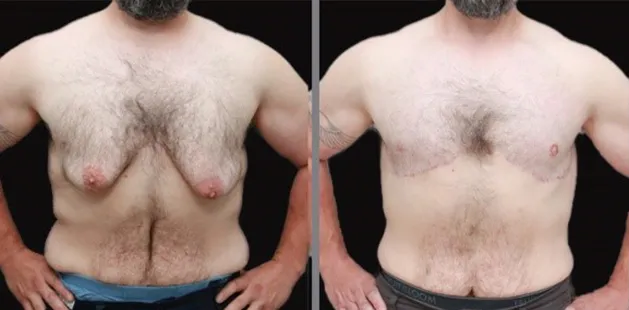
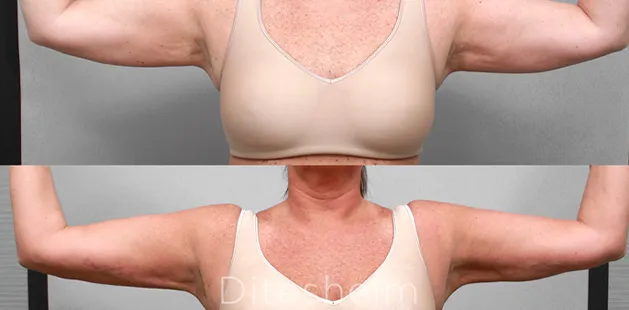
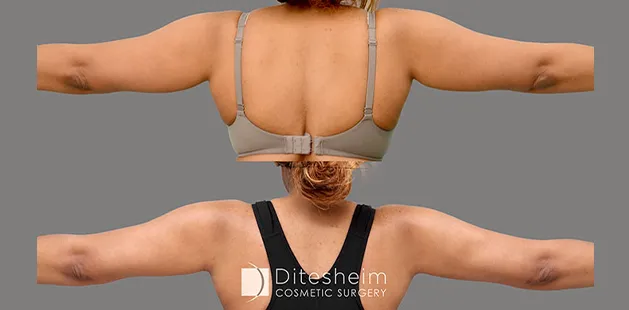
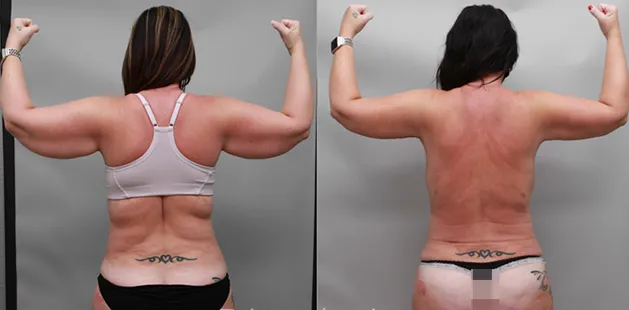
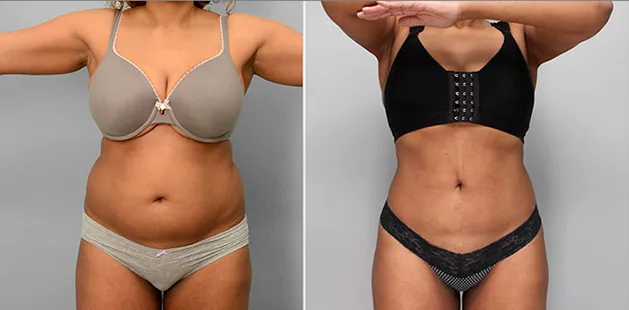
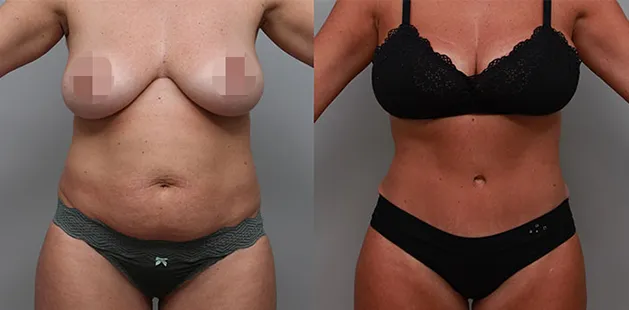
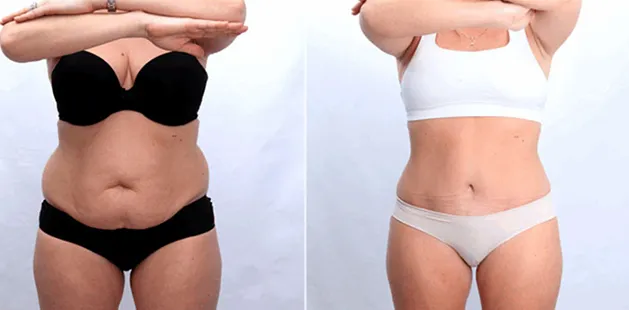
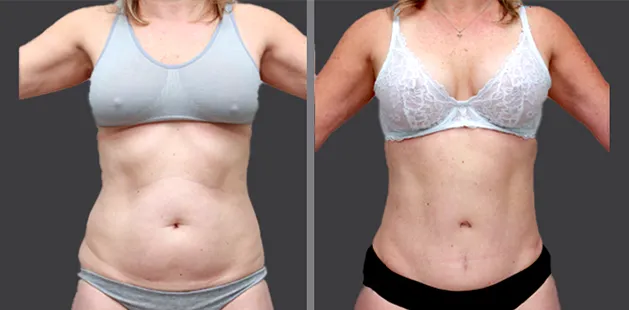
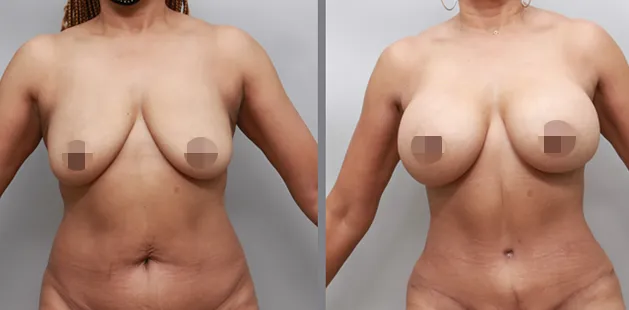
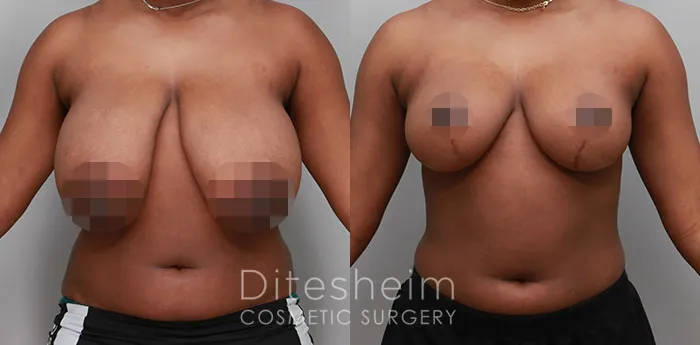
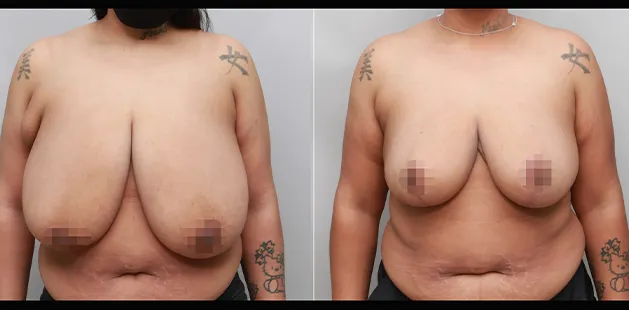
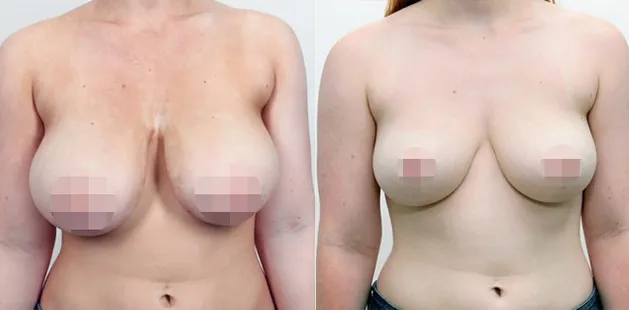
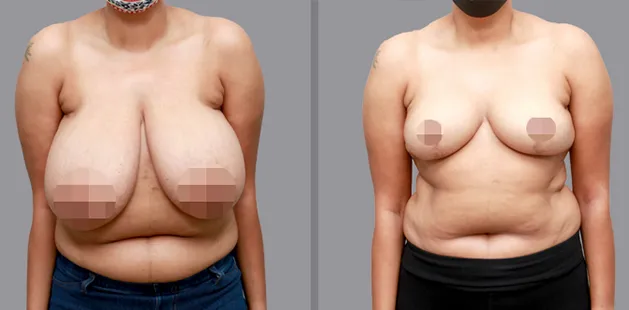
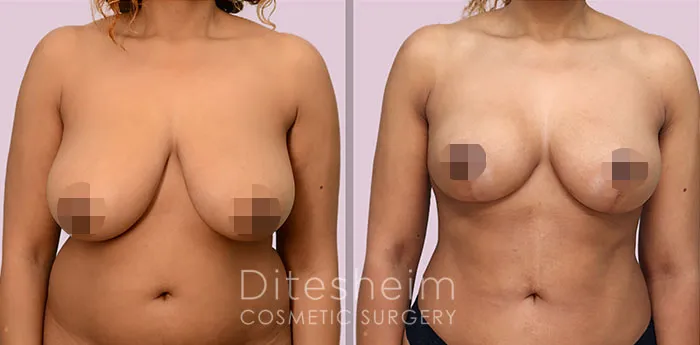
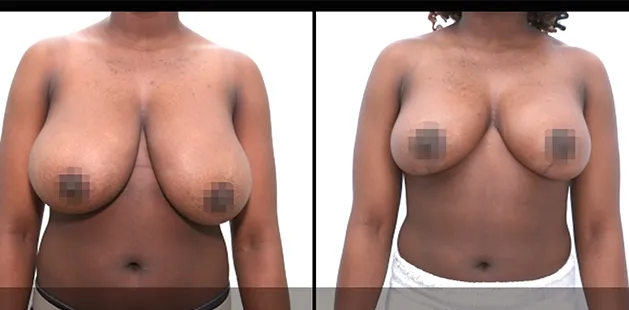
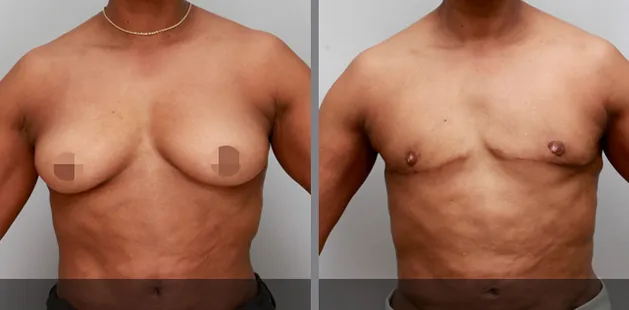
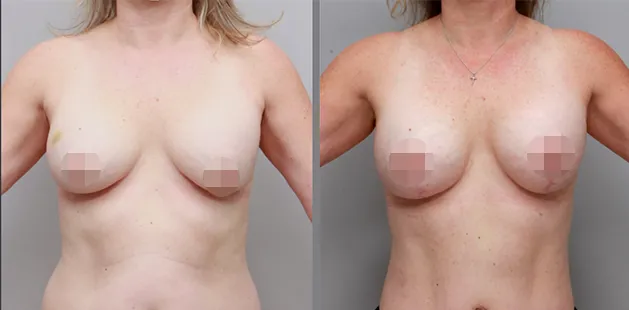
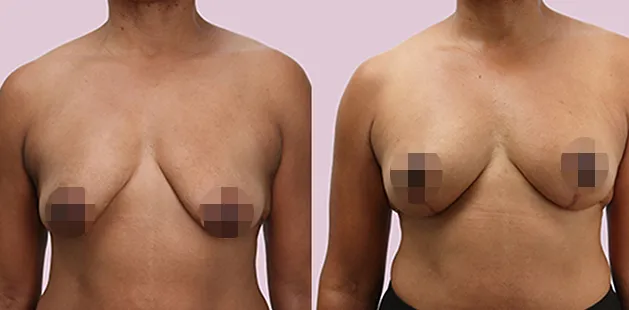
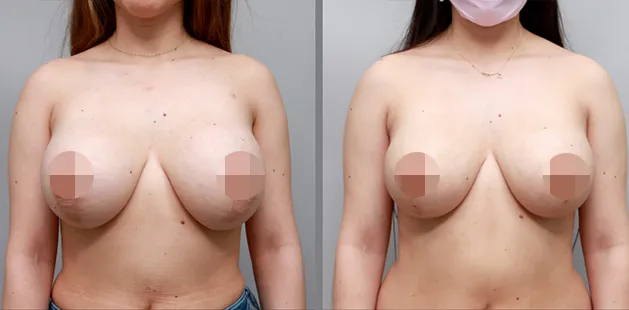
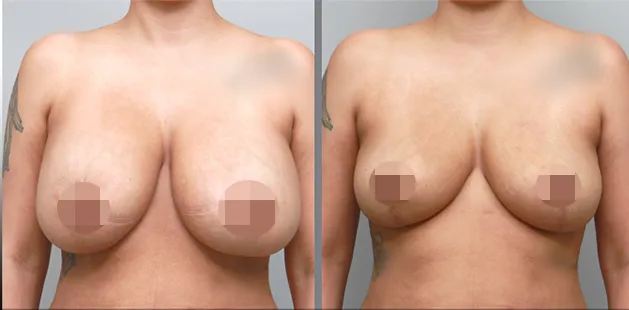
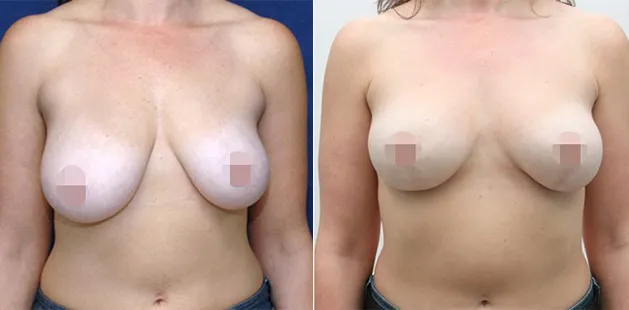
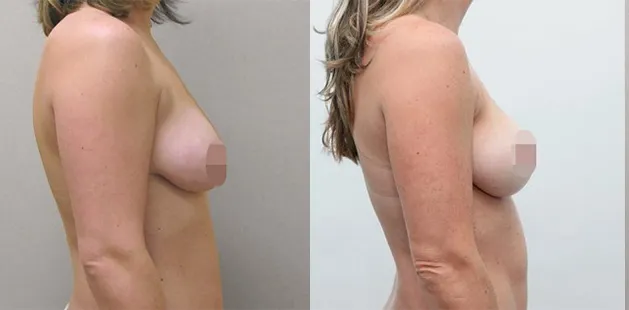
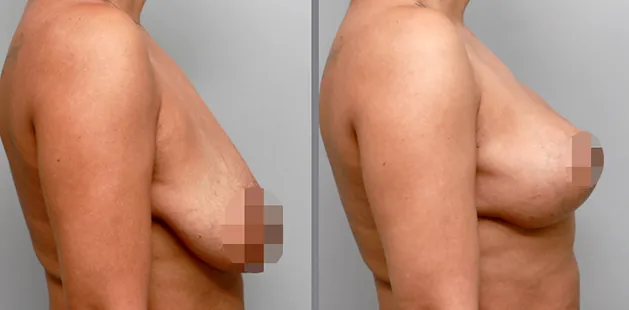
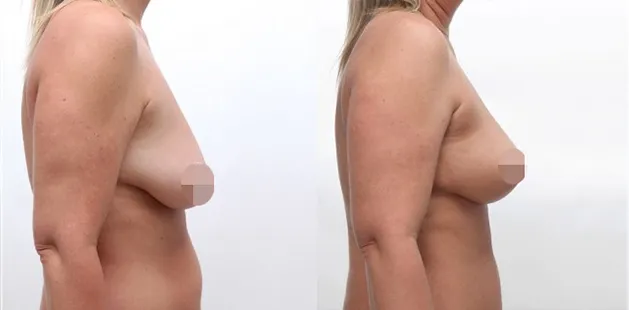
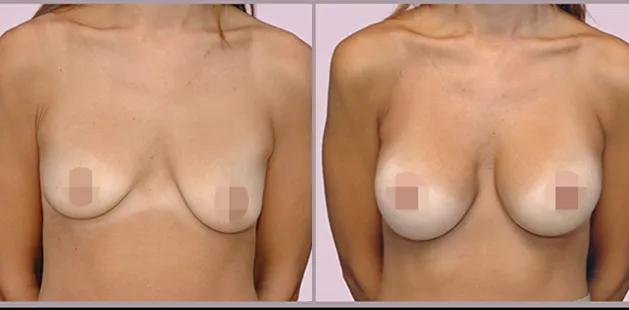
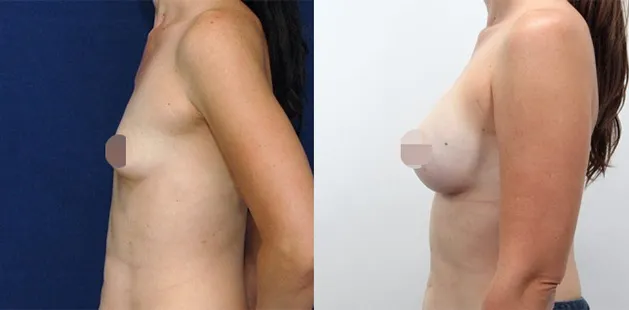
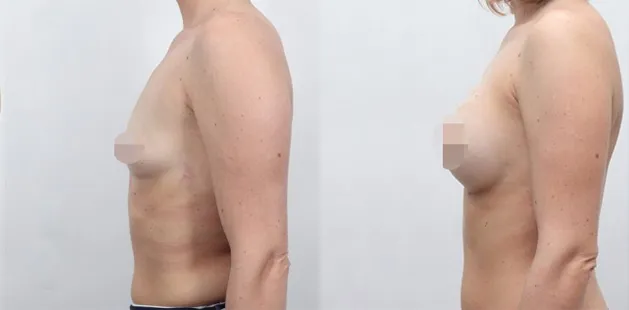
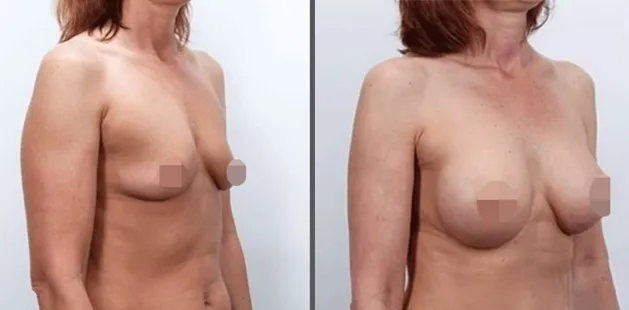
Gynecomastia Surgery
Excess chest tissue can make you feel uncomfortable in your own skin—even if you’re healthy and active. Gynecomastia surgery offers a permanent solution to restore confidence and a more masculine shape.
Gynecomastia Surgery at a Glance
Overview
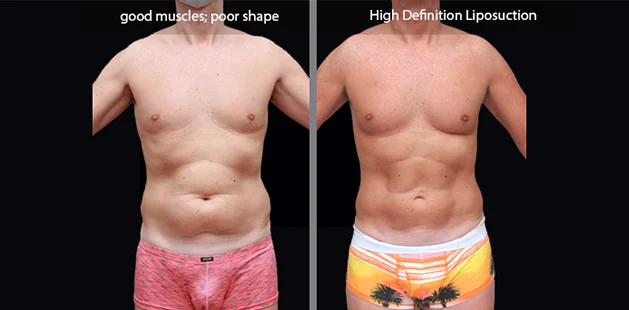
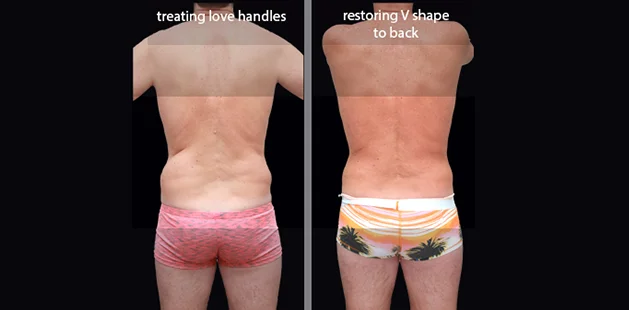
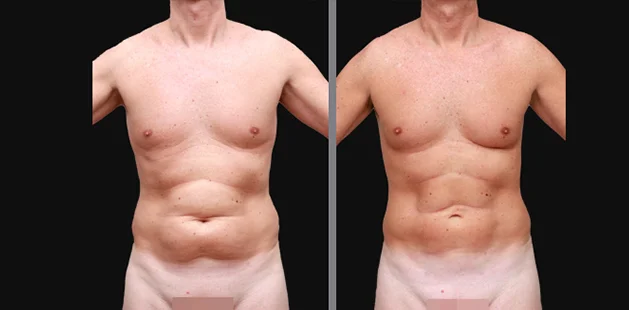
Gynecomastia surgery removes excess chest tissue to create a flatter, more masculine chest contour.
Recovery
Most patients return to light activity within a week, with swelling and soreness gradually improving over a few weeks.
Results
A firmed, more defined chest that looks natural and feels more like you.
Let Us Help You Identify the Problem
Grade One
Slight swelling around the nipple with minimal visible fullness. Often unnoticeable under clothing, but still frustrating.
Grade Two
More pronounced tissue extends beyond the areola but still blends into the chest wall. Noticeable in fitted shirts.
Grade Three
Tissue becomes more visible and defined. It may create a rounded chest shape that’s difficult to hide.
Grade Four
Significant tissue and excess skin create a visibly feminized chest. Often paired with weight loss or hormonal shifts.
Identify Your Grade
Let Us Help You Identify the Problem
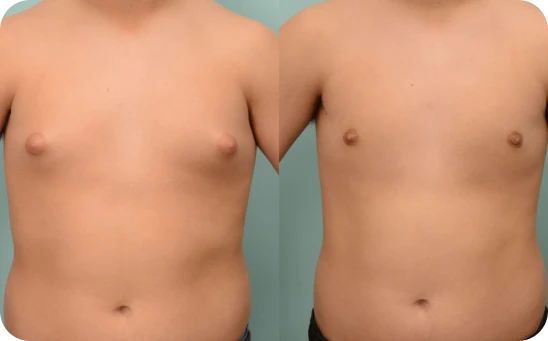
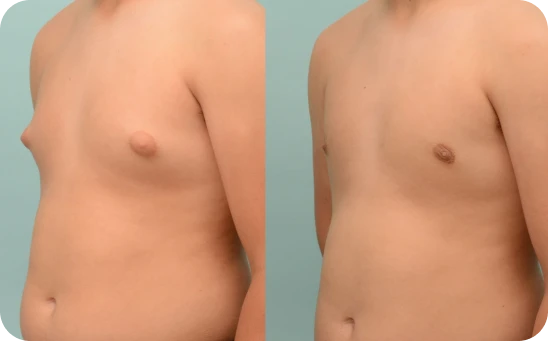
Grade One
Overgrowth of breast tissue below nipple
Grade 1 gynecomastia is the mildest form, with slight swelling around the nipples, some tenderness, and maybe a bit of puffiness or discoloration. It’s usually not noticeable under clothes, but might show when shirtless—like at the beach or pool.
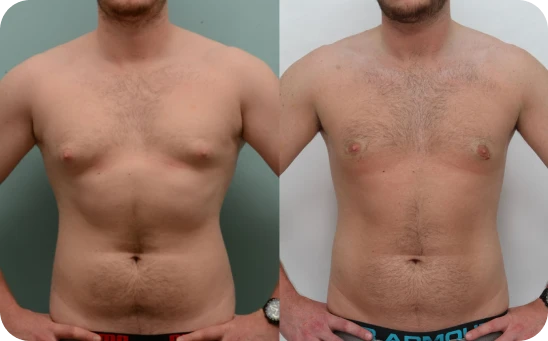
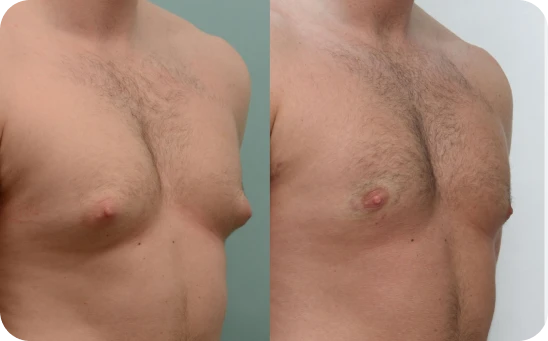
Grade Two
Breast tissue overgrowth giving breast shape
Grade 2 gynecomastia involves more noticeable breast growth that starts to spread across the chest, sometimes even showing through clothes. Puffiness and tenderness around the nipples can stick around too, which can make going shirtless feel uncomfortable or embarrassing.
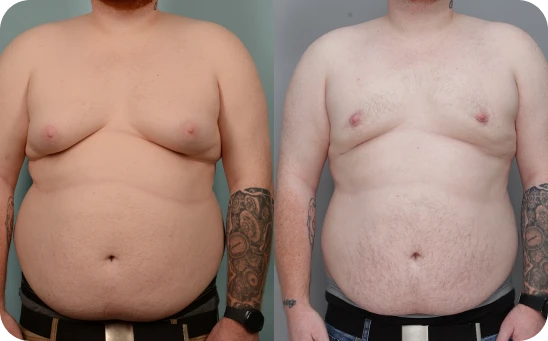
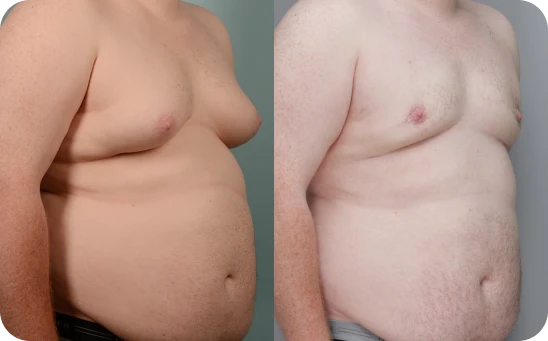
Grade Three
Nipple is below chest muscle border with more fatty tissue
At this stage, the chest looks fuller and droopier, often showing through clothes and making it hard to feel comfortable. At this stage, the changes can really affect confidence, and it’s common for people to start looking into treatment options.
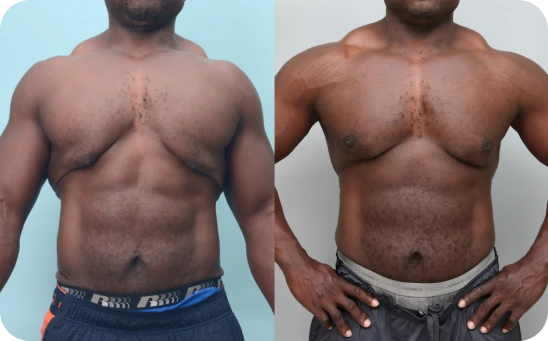
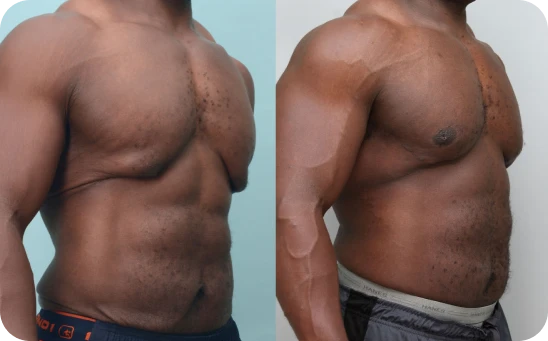
Grade Four
Ususally from weight loss and skin excess. Nipple slides below the chest muscle shape.
Grade 4 gynecomastia is the most severe form, where the chest takes on a noticeably feminine appearance with sagging, excess skin, and larger nipples. It can be hard to hide, even under clothes, and often causes emotional stress that makes treatment and support especially important.
Want to Learn More?
Gynecomastia Treatment in Charlotte, NC
Over-growth of male breast tissue commonly starts during adolescence or puberty and can persist into adulthood. Gynecomastia is quite common in teens, occurring in 4% of boys ages 10-19. After the age of 17, the persistence of male breast tissue is unlikely to disappear on its own and men will require surgical treatment with a male breast reduction surgery.
New Awake Procedure
Dr. Ditesheim’s new awake procedure corrects gynecomastia, restores a masculine chest with minimal scarring, and promotes a quick recovery. Dr. Ditesheim has designed an advanced gynecomastia treatment procedure that removes male breast augmentation with minimal or no scar on the chest, no drains, 1-3 day recovery, and no general anesthesia.
The goal of every gynecomastia procedure is the removal of the excess tissue and the restoration of a natural, masculine chest shape. Traditional surgical techniques meant larger incisions, drains, 6-8 weeks recovery, and sometimes unnatural chest shape.
Surgical Excision
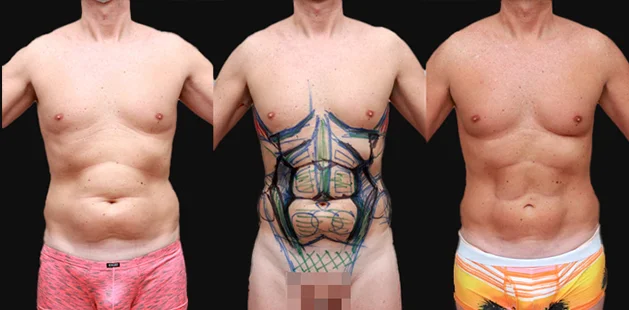
In complex gynecomastia patients where there is excess skin to remove, where nipple placement must be returned to a more natural position, or where the size of the areola must be reduced, excision techniques are used. Incisions for these procedures are either placed around the areola border or in the chest crease, following the chest muscle border depending on the complexity. (see Complex gynecomastia below)
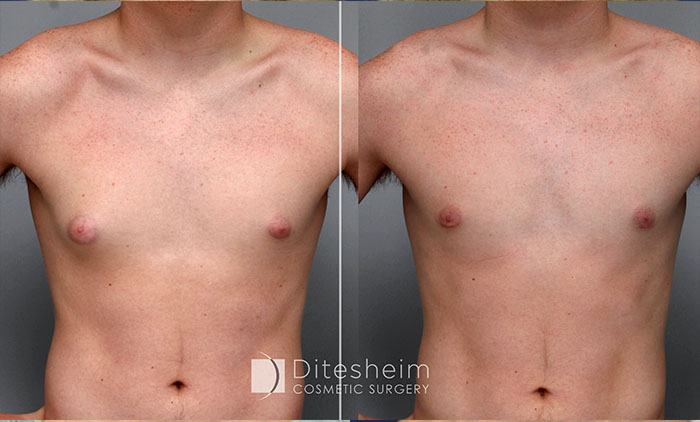
Advantages of Gynecomastia Treatment with Surgical Excision of Glandular Tissue:
- Scar is easily hidden around the nipple
- Awake procedure, able to drive home
- Quicker recovery, no drain, return to school or work 1-3 days.
Scarless Skin Tightening with Renuvion
Scarless Skin Tightening for an Even Better Result
If you’ve lost weight and are experiencing loose chest skin but want to avoid additional scarring, Renuvion may be a great option. This advanced technology tightens the skin from beneath the surface, helping it adhere more closely to the chest muscles—without creating a new scar.
Renuvion uses controlled heat delivered through a specialized probe, typically after gynecomastia surgery. The procedure takes an additional 30 to 60 minutes and can often be performed while awake.
This treatment is especially effective for men who have lost a moderate amount of weight (typically under 60 pounds), have lower nipple positioning (Grade 2 or 3), or are over the age of 50. However, if the nipple has dropped below the chest crease (Grade 4), surgical skin removal may be the better solution. Our clinic offers specialized care for Gynecomastia Treatment for Teens as well as cases caused by Gynecomastia from Steroids & Gym Supplements, ensuring safe and effective results.
Make the Change. See the Difference.
Testimonials
Real Patient Reviews
“I always had this issue with protruding male breast tissue that made me very self-conscious...being a bodybuilder, it was not always easy to take your shirt off...this was a great experience and I highly recommend. Dr. Ditesheim is the one for a happier YOU.”
“I had a great experience here! Dr. Ditesheim did an amazing job with my gynecomastia surgery...the surgery could not have been more smooth and I felt comfortable the whole time. The night after my surgery, Dr. Ditesheim even personally called to make sure everything was alright.”
“I chose Dr. Ditesheim for several reasons: his many years of experience with this surgery, his willingness to do a virtual consultation, [and] performing the surgery under local anesthesia which allowed me to drive myself...I felt no pain before, during, or after the surgery...it’s been over a year and nobody would know I had surgery...he truly nailed it.
“Staff was very welcoming and Dr. Ditesheim was very helpful in giving me an understanding of what Gynecomastia is and walked through the procedure. Also, made sure all my concerns and questions were answered.”
“Dr. Ditesheim and his entire staff were very knowledgeable and put me at ease (as this was my first cosmetic surgery ever). I was extremely pleased with the ease of the “awake” procedure for gyno removal.”
“Dr Ditesheim and his team had a lot of experience treating patients with my problem. I appreciated the minimally invasive methods that Dr Ditesheim uses to create outstanding results with almost nonexistent scarring.”
Recovery Timeline for Gynecomastia Surgery
1-3 Days
Rest and wear your compression vest. Mild soreness and swelling are normal. Most patients manage discomfort with over-the-counter meds.
1 Week
You can return to light activity or work. Compression garment still worn. Bruising fades
2-3 Weeks
Most swelling resolves. You’ll start to see early results. Avoid upper body workouts or heavy lifting.
4-6 Months
Resume exercise. Chest appears flatter, more sculpted, and natural.
3-6 Months
Final results set in as tissues heal and settle. Scars continue to fade.
1-3 Days
Rest and wear your compression vest. Mild soreness and swelling are normal. Most patients manage discomfort with over-the-counter meds.
1 Week
You can return to light activity or work. Compression garment still worn. Bruising fades
2-3 Weeks
Most swelling resolves. You’ll start to see early results. Avoid upper body workouts or heavy lifting.
4-6 Months
Resume exercise. Chest appears flatter, more sculpted, and natural.
3-6 Months
Final results set in as tissues heal and settle. Scars continue to fade.
View Our Pricing
Upfront, Honest, No Guesswork.
Each surgical plan is personalized, so your exact pricing may vary. Additional options like fat grafting, Renuvion (scarless skin tightening), high-definition etching (to enhance muscle definition), higher BMI considerations (over 32), or an overnight stay may affect the total cost.
Get Pricing
I’m interested in:
Three Simple Steps to a Custom-Tailored Plan
Your Consultation Journey Starts Here
At Ditesheim Cosmetic Surgery, your consultation is more than a conversation — it’s a process built around you. In just three clear steps, we listen to your goals, evaluate your needs, and present surgery plan options designed to fit your lifestyle, body, and vision.
01
Book Your Consultation
Meet with our team to talk through your goals, concerns, and vision—no pressure, just support.
02
Explore Your Options
We’ll walk you through the possibilities and explain what’s realistic for your body and lifestyle.
03
Build Your Surgical Plan
Your treatment plan is fully customized around you—designed to deliver results that feel natural and lasting.
01
Book Your Consultation
Meet with our team to talk through your goals, concerns, and vision—no pressure, just support.
02
Explore Your Options
We’ll walk you through the possibilities and explain what’s realistic for your body and lifestyle.
03
Build Your Surgical Plan
Your treatment plan is fully customized around you—designed to deliver results that feel natural and lasting.
Schedule Your Consultation for Gynecomastia Treatment in Charlotte
The consultation is a confidential meeting for you to meet with Dr. Ditesheim. He will answer your questions, examine you and give you a personal plan to address your gynecomastia condition. At your consultation, you will be given exact fees for your procedure and detailed instructions to prepare for the procedure and aftercare. Ditesheim Cosmetic Surgery performs gynecomastia surgery in Charlotte, NC, and surrounding areas. Call or contact us online to schedule your consultation today.
Gynecomastia FAQs
Still have questions? Here are some of the most common questions we get from patients considering body contouring procedures:
What causes gynecomastia in males?
Can liposuction be used to treat male breasts?
For patients whose gynecomastia is mostly excess fatty tissue, Aquashape (water-assisted liposuction) or Vaser (ultrasound-assisted liposuction) can be used to remove the excess fat.
Who is a good candidate for gynecomastia surgery with liposuction?
What is the recovery? When can you go back to the gym? Or work?
With Dr. Ditesheim’s surgical technique, most men recover in three days or less. You can return to work in one to three days. We ask that you hold off on exercise and strenuous activities for one to two weeks.
Do stitches need to be removed? How will the skin not be saggy?
Will you need skin removed?
Will you need general anesthesia for this surgery?
Will there be drains?
No. Dr. Ditesheim’s advanced surgical technique for the treatment of male gynecomastia does not involve drains.
Will you need a compression vest postop?
Will you be ok for a vacation in one month?
What is the cost?
How does Dr. Ditesheim do the procedure?
Will Dr. Ditesheim take out all the breast tissue?
Will the gynecomastia come back?
Will there be a change in nipple sensation?
Where are the scars?
Sometimes, Dr. Ditesheim performs gynecomastia surgery that only requires liposuction through a small incision in your armpit. If glandular tissue needs to be removed, you will have a small scar just below your nipple at the areola border or in your natural chest crease. These types of scars are easily hidden. For patients requiring excess skin removal, Dr. Ditesheim will show you exactly where he plans to leave a scar. Rest assured that Dr. Ditesheim always has the best cosmetic results in mind, so incisions are made in places where the scars will fade into your natural contours.
Always remember that we are here to answer your questions. If you are still wondering about some aspect of your surgery or recovery, call our clinic today or ask Dr. Ditesheim on the day of your surgery.